Complete Breakdown of Intake, Air Conditioning & Air-Related Components
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn everything about air system components in a car — from what they are, how they work, why they matter, and how to maintain them. We include clear explanations, visuals, and links to authoritative resources. Car Air System Parts
Introduction: Why Air Matters in a Car Car Air System Parts
Air isn’t just something your car breathes — it’s vital to both performance and comfort.
There are two major air-related systems in every modern vehicle: Car Air System Parts
- Air Intake System — feeds clean air into the engine for combustion. Car Air System Parts
- Air Conditioning (A/C) System — delivers cool, filtered, and comfortable air into the cabin. Car Air System Parts
Both involve many parts working in harmony. Proper care extends engine life, fuel efficiency, and comfort levels — whether you’re driving across town or on a long road trip.
🧰 Section 1: Engine Air Intake System — Feeding the Engine

4
What Is the Air Intake System?
The air intake system’s job is simple: gather fresh outdoor air, clean it, and deliver it to the engine’s combustion chambers. Without this system, the engine would draw dirty air that can damage internal components.
The typical intake path goes like this:
Outside Air ➜ Air Filter ➜ Intake Tube/Pipe ➜ MAF/Pressure Sensors ➜ Throttle Body ➜ Intake Manifold ➜ Engine Cylinders
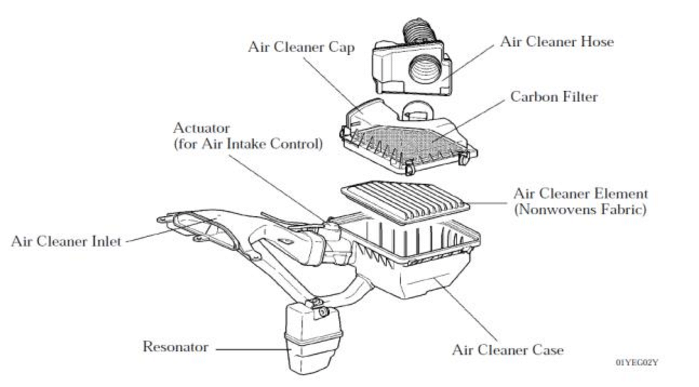
1. Air Filter & Airbox
The air filter traps dust, debris, and contaminants before they can enter the engine. It sits inside a protective box called the airbox.
- Filters should be changed regularly — usually every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, depending on driving conditions.
- A dirty filter reduces airflow, hurting engine performance and fuel efficiency.
For details on airboxes (the chamber that houses the filter and channels airflow):
🔗 Airbox — Wikipedia article (external link)
2. Intake Tube / Intake Hose
After the filter, clean air travels through the intake tube or intake hose toward sensors and the throttle body. These hoses must be airtight; cracks can introduce unfiltered air or confuse engine sensors. Car Air System Parts
3. Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor & MAP Car Air System Parts
Modern cars use sensors to measure exactly how much air is coming in: Car Air System Parts
- MAF (Mass Air Flow) Sensor — measures the mass of incoming air. Car Air System Parts
- MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) Sensor — helps calculate air density inside the intake. Car Air System Parts
Without accurate airflow data, the engine can’t balance fuel and air properly. Car Air System Parts
4. Throttle Body & Intake Manifold Car Air System Parts
- The throttle body controls how much air enters the engine. Car Air System Parts
- The intake manifold distributes that air evenly to each cylinder. Car Air System Parts
Together they influence how the engine responds when you accelerate or idle. Car Air System Parts Car Air System Parts
5. Air Temperature & Intake Control Car Air System Parts
Some systems include a heated air inlet designed to alter intake air temperature for emissions efficiency, especially during cold starts. Car Air System Parts
🔗 Heated Air Inlet — Wikipedia article Car Air System Parts
Why This Matters Car Air System Parts
A well-designed intake system:
- Improves power and acceleration
- Enhances fuel efficiency
- Reduces emissions
- Protects the engine from contaminants
🌬️ Section 2: Car Air Conditioning (A/C) System — Comfort Inside the Cabin
4
What Is the A/C System?
Your car’s air conditioning does more than cool the cabin — it also filters and dehumidifies air for comfort and safety. In hotter climates, a functioning A/C system prevents heat stress and improves driver focus.
According to automotive parts experts, the A/C system is made up of a range of components working to compress, cool, and circulate refrigerant.
Major A/C Components
Let’s break these down:
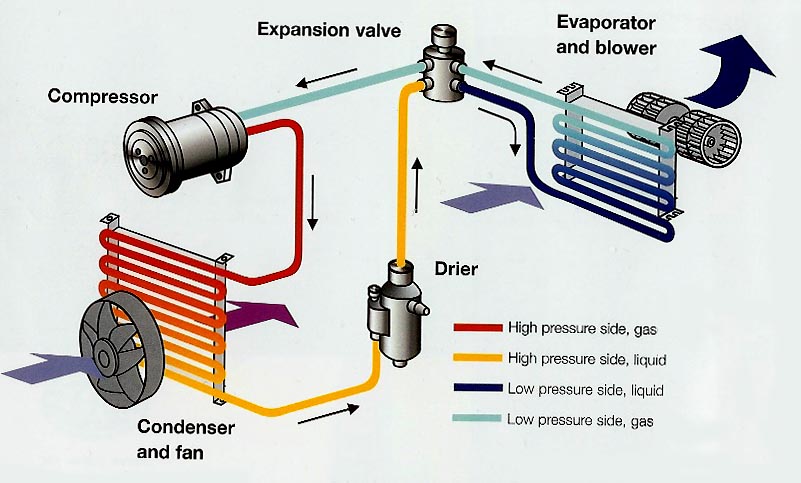
❄️ 1. Compressor — The Heart of the A/C
The A/C compressor pressurizes and circulates refrigerant through the system. It’s driven by the engine via a belt.
- Without the compressor, the refrigerant won’t flow — and no cooling happens.
- This part often fails due to wear or low refrigerant.
📌 Signs of compressor issues: weak cooling, strange noises, warm air. (Reddit auto-mechanic reports)
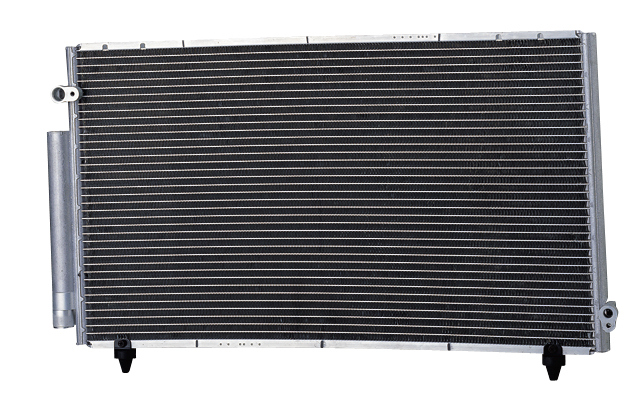
🔄 2. Condenser
Located near the front of the vehicle, this component cools the high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor and turns it into a liquid.
🚿 3. Expansion Valve / Orifice Tube
Controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. Without it, refrigerant would flow too quickly or too slowly, reducing cooling efficiency.
❄️ 4. Evaporator
Inside the dashboard, the evaporator absorbs heat from cabin air, cooling it before blowing it through the vents.
🍃 5. Blower Motor & Cabin Filter
- The blower motor pushes cooled or heated air into your cabin.
- The cabin filter removes dust and pollen before air enters.
⚙️ 6. Receiver/Drier or Accumulator
These components remove moisture from the refrigerant to prevent freezing or corrosion.
Secondary A/C Parts
There are additional supporting parts like:
- Pressure switches
- Hose assemblies
- Electronic control modules
- HVAC actuators and sensors
External Resources for A/C Parts
Here are well-known online suppliers where auto technicians and DIYers can explore parts:
- 🔗 AutoAirOnline – Automotive A/C parts catalog (external shop)
- 🔗 CARiD – Car A/C & heating parts (external catalog)
- 🔗 EuropeanAutoSpares – Aftermarket air conditioning parts (external shop)
- 🔗 Aircoparts.net – Full AC parts lineup (external shop)
These sites help you find OEM-equivalent and aftermarket replacements by vehicle make and model.
🔍 Section 3: How a Car Air System Works (Step-by-Step)
This part explains operation flow in easy terms.
🏁 Air Intake Flow (Engine)
- Outside Air enters through the intake.
- Air Filter removes particulates.
- Sensor Measurement (MAF/MAP) sends data to the ECU.
- Throttle Body regulates airflow based on throttle position.
- Intake Manifold distributes air to each cylinder.
- Combustion Occurs, power is produced.
Proper airflow ensures efficient fuel combustion and lower emissions.
🌡️ A/C Refrigerant Cycle
- Compressor pressurizes refrigerant gas.
- Condenser cools gas into liquid.
- Expansion Valve meters liquid refrigerant.
- Evaporator absorbs cabin heat, returns to gas.
- Cycle repeats to extract more heat.
🛠️ Section 4: Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Keeping air systems healthy extends car life and comfort.
When to Replace Intake Parts
Signs to inspect or replace:
- Reduced engine power
- Rough idle
- Poor fuel economy
- Dirty or clogged air filter
Replace filters as per manufacturer recommendations, and inspect hoses for cracks.
Common A/C Problems & What They Mean
Many drivers report common symptoms when A/C parts fail:
- Weak airflow — possible blower motor or clogged cabin filter
- Warm air instead of cold — low refrigerant or failing compressor
- Odd noises — worn compressor or loose belt
- Musty odor — mold in evaporator, replace cabin filter
- Moisture or leaks — refrigerant or condenser leak
🧠 Section 5: Buying Guide & Tips
When shopping for parts:
- Always match your vehicle’s make, model, year, and engine size.
- Choose OEM or high-quality aftermarket for durability.
- Check warranty coverage (many A/C parts have 1-year warranties).
- Consider professional installation for AC compressors and refrigerant lines.
📌 Conclusion: Air Systems Keep Your Car Healthy

The air intake and AC systems are fundamental to your car’s performance and comfort. Understanding each part — from filters to compressors — empowers you to diagnose issues, maintain your vehicle, and make informed decisions about repairs and upgrades.
Internal & External Links to Use on Your Site
Internal (replace with your site pages):
- /car-maintenance/air-filter-replacement
- /car-ac-service/diagnosis-tips
- /intake-vs-exhaust-systems-explained
External (already cited):
- Wikipedia: Airbox —
- Heated Air Inlet —
- AutoAirOnline – Automotive A/C Parts
- CARiD – Car A/C Parts
- EuropeanAutoSpares – Aftermarket A/C Parts
- Aircoparts.net – A/C Components
📸 Optional Image Credits & Alt Text
You may add your own images using alt text like:
alt="Car air intake system diagram"alt="Automotive AC compressor installed in engine bay"alt="Cabin air filter replacement example"
If you want, I can generate downloadable graphics, SEO meta descriptions, or shorter social posts based on this article to help you publish fast! 🚙 5. Air Temperature & Intake Control
Air temperature plays a critical role in how efficiently an engine performs. The Air Temperature & Intake Control system ensures that the air entering the engine is at the optimal temperature and density for combustion, power output, and emissions control.
🔥 Why Air Temperature Matters
Engines rely on a precise air-fuel mixture. The temperature of incoming air directly affects its density:
- Cooler air = denser air = more oxygen molecules = stronger combustion
- Warmer air = less dense air = reduced oxygen = lower power
Because of this, managing intake air temperature helps maintain:
- Stable engine performance
- Better fuel efficiency
- Lower emissions
- Improved cold-start behavior
🌡️ Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor measures the temperature of air entering the engine. It sends data to the Engine Control Unit (ECU), which adjusts:
- Fuel injection timing
- Air-fuel mixture ratio
- Ignition timing
In many modern vehicles, the IAT sensor works together with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor to ensure accurate air measurement.
📌 If the IAT sensor fails, you may notice:
- Poor fuel economy
- Rough idling
- Check Engine Light
- Reduced power
❄️ Cold Air vs Warm Air Intake
Some vehicles use systems that regulate whether the engine receives warmer or cooler air depending on conditions.
A traditional example is the Heated Air Inlet, which allows warmer air into the engine during cold weather to improve combustion and reduce emissions during startup.
Modern systems may use:
- Variable intake ducts
- Electronic flaps
- Temperature-controlled air routing
These systems balance efficiency and environmental requirements.
🌬️ Air Intake Control Valve
Certain engines include an air intake control valve that adjusts airflow speed and direction inside the intake manifold. This helps:
- Improve torque at low RPM
- Enhance power at high RPM
- Optimize combustion efficiency
By controlling air velocity, the engine maintains better responsiveness across different driving conditions.
🚗 Turbocharged & Performance Engines
In turbocharged vehicles, intake air temperature becomes even more important. Compressing air raises its temperature, which reduces density. To counter this, engines use an intercooler to cool compressed air before it enters the engine.
Benefits include:
- Increased horsepower
- Reduced engine knock
- Improved fuel efficiency
⚙️ Symptoms of Intake Temperature Problems

If intake temperature control isn’t functioning properly, drivers may experience:
- Engine knocking or pinging
- Sluggish acceleration
- Increased fuel consumption
- Rough cold starts
- Check Engine Light warnings
Regular diagnostics and sensor checks help prevent long-term engine damage.
🛠️ Maintenance Tips
To keep your air temperature & intake control system working properly:
- Replace the air filter regularly
- Inspect intake hoses for cracks or leaks
- Clean the MAF sensor when necessary
- Ensure sensors are properly connected
- Check intercooler condition (if turbocharged)
📌 Final Thoughts
Air temperature and intake control systems may seem small compared to major engine components, but they play a vital role in performance, efficiency, and emissions control. By monitoring and adjusting incoming air temperature, modern vehicles maintain smooth operation in both hot summers and cold winters.
Understanding this system helps drivers make smarter maintenance decisions — and ultimately keeps the engine running at peak efficiency. 🚘